Exposure time calculation in RT is very important to perform radiography tests and develop radiographs meeting the standard requirements. Exposure time is the time required for sufficient radiation energy to ionize the film emulsion to the desired density after processing.
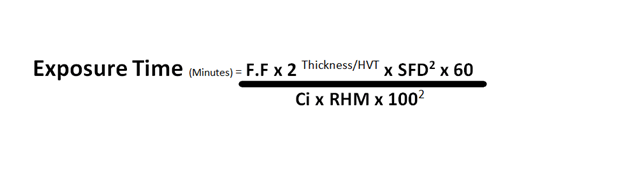
F.F ( Film factor )
Film Factor by definition is: Amount of Exposure (R) per unit area of the Film required to produce a desired optical density. And Inverse of the Film Factor is Film Speed. Unit of Film Speed is 1/R.
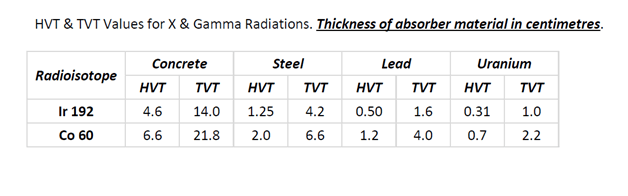
Film factors of Carestream films
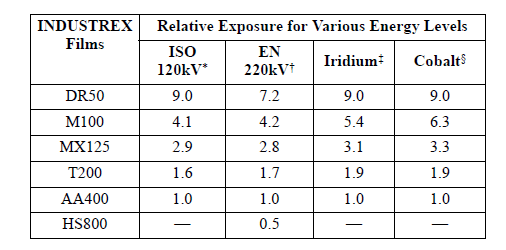
HVT: Half value thickness
Half Value Thickness (HVT): The thickness of a material, usually called an absorber, needed to reduce the intensity of radiation to half its initial value is known as half-value thickness.
Tenth Value Thickness (TVT): Thickness of any material needed to reduce the intensity of radiation to one-tenth its initial value is known as tenth value thickness.
Thumb rule: 1 TVT = 3.3 HVT
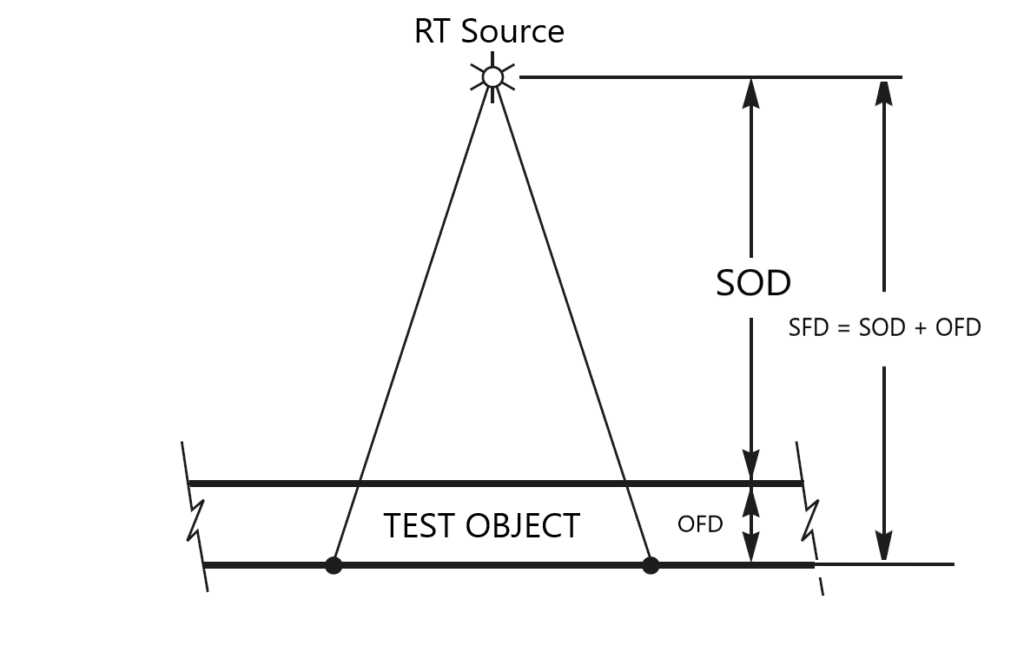
Source to film distance (SFD)
SFD – Source-to-Film Distance – is the distance between the radiation source and the film in radiographic testing, as measured in the direction of the beam.
SFD = SOD + OFD
OFD – Object-to-Film Distance – is the distance between the radiation source and the radiation side of the test object, measured along the central axis of the radiation beam.
SOD – Object-to-Film Distance – is the distance between the radiation side of the test object and the film surface, measured along the central axis of the radiation beam.
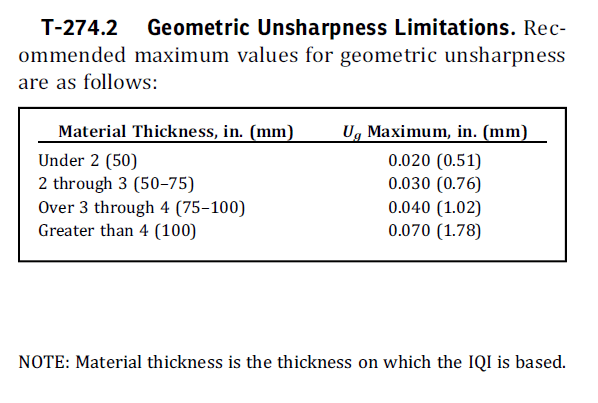
Geometric unsharpness: It refers to the loss of definition resulting from geometric factors of the radiographic equipment and setup. It occurs because the radiation does not originate from a single point but rather over an area.
geometric unsharpness: the penumbral shadow in a radiological image, which is dependent upon
- (a) radiation source dimensions
- (b) source-to-object distance
- (c) object-to-detector distance
SFD can be calculated from the Ug formula given below.

Curie (Ci): Curie is the unit of radioactivity (decay of source).
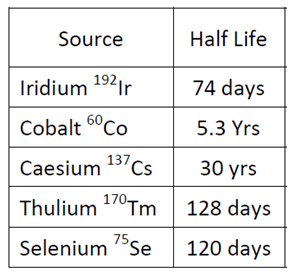
Curie value can be obtained from the decay chart of the source or calculated using the half-life of the radioactive source.
Present Activity (A) = Ao/ 2n
Where Ao = Initial Activity
n= Time / HVT
HL (half-life ):
Each isotope has a “half-life”- a length of time by which half (50%) of the radioactive isotope has decayed into a stable element – two half-lives mean the source has only 25% of its original strength, three half-lives 12.5%.
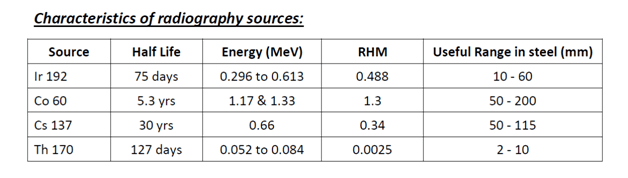
RHM:
Roentgen(unit of exposure) per hour at 1 meter for the source being used.
References :
- ASME BPVC Sec-V
- https://www.nde-ed.org/
- www.bindt.org
- TWI global
To learn basics about Radiography testing read our blog :
Amazing detailed explanation. Kudos 👌👍
Shooting with Ir92 – 70curies a 0.643″ thick plate at 16″ SFD with MX film: what do you guys get for time?
around 2.30 Minutes
3.1 X 1.428 X 16 SQ X 60 / 70 X 0.488 X 100 SQ = 1.990 ???
Dears::
Exposure Time (in minutes) = 0.199 minute
0.199 * 60 sec = 11.94 seconds ???
2.22 min,=133.28sec
1″ pipe SS thk 3.38 – timeline of 1 joint with IR192
How can I calculate the exposure time for directional X-ray tube of 250kva for 16” sch 40
for X ray exposure time calculation you will have to use the exposure time chart provided by your X ray machine manufacturer.