The welding inspector is a responsible person, involved in the determination of weld quality according to applicable codes and/or specifications. The welding inspector is one of the “front line” individuals who must check to see if all of the required manufacturing steps have been completed properly.
Welding inspection is done in the construction of buildings, bridges and other structural units. Energy related applications include power generation facilities, pressure vessels and pipelines, and other distribution equipment requiring pressure containment. The chemical industry also uses welding extensively in the fabrication of pressure-containing processing facilities and equipment. The transportation industry requires assurance of accurate weld quality in such areas as aerospace, automotive, shipbuilding, railroad apparatus and off-road equipment.
Welding inspector roles and responsibilities
the welding inspector plays a large role in any successful welding quality control program, however he is not singularly responsible for the attainment of weld quality. the welding inspector must have a wide range of knowledge and skills, because it involves more than simply looking at welds in order to do his job effectively.
To learn more about Welding process and other metal joining technology read out blog :
The welding inspector must be familiar with many facets of the fabrication process.
Before welding, the inspector will check drawings and specifications to determine such information as the configuration of the component, its specific weld quality requirements and what degree of inspection is required. This review will also show the need for any special processing during manufacturing.
Once welding begins, the welding inspector may observe various processing steps to assure that they are done properly. If all these subsequent steps have been completed satisfactorily, then final inspection after welding should simply confirm the success of those operations.
The three general categories into which the welding inspectors’ work functions can be grouped are:
• Overseer – The Overseer is usually one who oversees the duties of several inspectors.
• Specialist – The specialist, on the other hand, is an individual who does some specific task(s) in the inspection process.
• Combination Overseer—Specialist – Usually inspectors serving as both overseer and specialist. Such an individual aree responsible for general weld quality judgments in each of the various fabrication steps, and be required to perform any nondestructive testing that is necessary.
Important Qualities
The Inspector Possesses a Great Amount of Knowledge, Attitudes, Skills, and Habits (KASH)
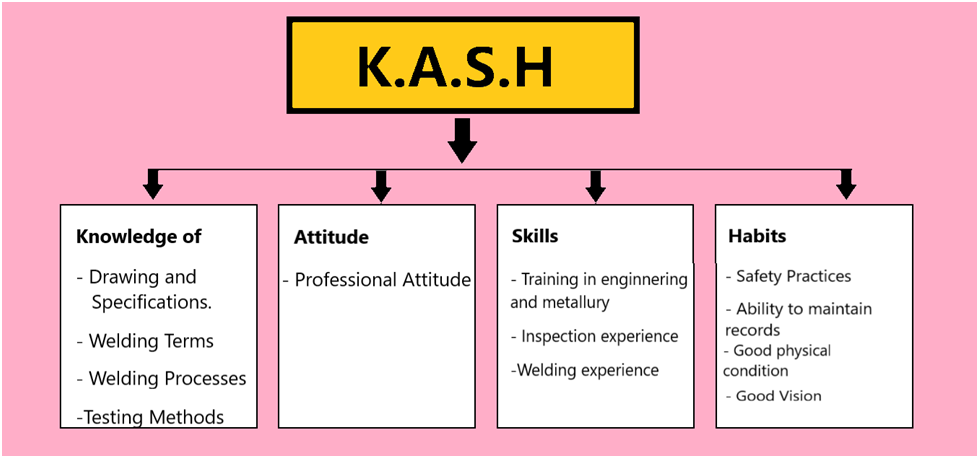
Welding inspector must be completely familiar with the job requirements. Inspection decisions must be based on facts; the condition of the weld and the acceptance criteria specified in the applicable specification must be the determining factors. Inspectors will often find themselves being “tested” by other personnel on the job, especially when newly assigned to some task. Maintaining a professional attitude helps overcome obstacles to successful job performance. The individuals performing welding inspection must possess certain qualities to assure that the job will be done most effectively.
Since the primary job involves visual inspection, obviously the welding inspector should have good vision, whether natural or corrected. The AWS CWI program requires the inspector to pass an eye examination, with or without corrective lenses, to prove near vision acuity on Jaeger J2 at not less than 12 in, and complete a color perception test. The welding inspector should be in good physical condition.
Welds can be located anywhere on very large structures, and inspectors must often go to those areas and make evaluations. Inspectors should be in good enough physical condition to go to any location where the welder has been. Within safety guidelines, they should not let their physical condition prevent them from doing the inspection properly.
Another important quality the welding inspector is an ability to understand and apply the various documents describing weld requirements. These can include drawings, codes, standards and specifications. Documents provide most of the information regarding what, when, where and how the welding and subsequent inspections are to be done.
Therefore, the rules or guidelines under which the welding inspector does the job can be found in these documents. They also state the acceptable quality requirements against which the welding inspector will judge the weld quality. It is important that these documents are reviewed before the start of any work or production because the welding inspector must be aware of the job requirements.
Work Experience will aid the welding inspector in becoming more efficient. Better ways of thinking and working will develop with time. Work Experience will also help the inspector develop the proper attitude and point of view regarding the job. Experience gained working with various codes and specifications improves an inspector’s understanding of welding requirements and generally improves job effectiveness.
Another desirable quality of the welding inspector is a basic knowledge of welding and the various welding processes Because of this, former welders are sometimes selected to be converted into welding inspectors. With a basic knowledge of welding, the inspector is better prepared to understand certain problems that a welder encounters. This aids in gaining respect and cooperation from the welders.
It also helps in understanding the welding inspector to predict what weld discontinuities may be encountered in a specific situation. The welding inspector can then monitor critical welding variables to aid in the prevention of these welding problems. Inspectors experienced in several welding processes, who understand the advantages and limitations of each process, can probably identify potential problems before they occur.
Knowledge of various destructive and nondestructive test methods is also very helpful to the welding inspector. Although inspectors may not necessarily perform these tests, they may from time to time witness the testing or review the test results as they apply to the inspection. Just as with welding processes, the welding inspector is aided by a basic understanding of testing processes.
It is important for the inspector to be aware of alternate methods that could be applied to enhance visual inspection. Welding inspectors may not actually perform a given test but they may still be called upon to decide if the results comply with the job requirements.
The ability to be trained is a necessity for the job of welding inspector. Often, an individual is selected for this position based primarily on this attribute. Inspectors do their job most effectively when they receive training in a variety of subjects. By gaining additional knowledge, inspectors become more valuable to their employers.
Another very important responsibility of the welding inspector is safe work habits; good safety habits play a significant role in avoiding injury. Working safely requires a thorough knowledge of the safety hazards, an attitude that all accidents can be avoided, and learning the necessary steps to avoid unsafe exposure. Safety training should be a part of each inspector’s training program.
A final attribute, which is not to be taken lightly, is the ability to complete and maintain inspection records. They must accurately communicate all aspects of the various inspections, including the results. All records developed should be understandable to anyone familiar with the work When reports are generated, they should contain information regarding how the inspection was done.
Ethical Requirements – the welding inspector should act with complete honesty and integrity while doing the job since the inspection function is one of responsibility and importance. A welding inspector’s decisions should be based totally on available facts without regard to who did the work in question.
A Communicator – the welding inspector has to communicate with several different people involved in the fabrication sequence. In fact, many situations occur where they are the central figure of the communication network, since they will constantly be dealing with most of the people involved. Some people that the inspector may communicate with are welders, welding engineers, inspection supervisors, welding supervisors, welding foremen, design engineers, and production supervisors.
Personnel Certification Programs
AWS QC1, Standard for AWS Certification of Welding Inspectors, and AWS B5.1, Specification for the Qualification of Welding Inspectors, establish the requirements for AWS qualification and certification of welding inspection personnel. There are three levels of certification in AWS QC1.
The Senior Certified Welding Inspector (SCWI) is a person with at least 15 years experience, including 6 years experience while certified as a Certified Welding Inspector (CWI). The SCWI must pass a separate examination from the CWI examination explained below. Information on the SCWI program and examination are found in a separate course, Welding Quality Assurance and Inspection Manual—A Guide for the Senior Certified Welding Inspector.
The next certification level is the CWI and the third level is the Certified Associate Welding Inspector (CAWI). Both of these certifications are covered in this course. AWS QC1 and AWS B5.1 describe how personnel are qualified and certified, lists the principles of conduct, and notes the practice by which certification may be maintained.
References:
WELDING INSPECTION TECHNOLOGY FIFTH EDITION—2008 Published by American Welding Society Education Department
Feature Image : Photo by Benjamin Wedemeyer on Unsplash
