There are no precise dates recorded as to when NDT began as a recognized technology, human beings have performed nondestructive tests from their beginning. Centuries before the expression NDT was first used, people “looked” at objects to determine size, shape, and even the presence of visual surface imperfections and “listened” to the metal being shaped by a blacksmith or the tone of a bell after it was cast.
World War II had the greatest effect on the technology and devices that are used today. World War II (often abbreviated to WWII or WW2), also known as the Second World War, was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. Technology also played a greater role in the conduct of World War II than in any other war in history and had a critical role in its final outcome. During this period different methods of NDT prominently came to use in the Mechanical world, However, there is no precise dates are recorded as to when NDT began as a recognized technology but it was used by human beings from centuries in different forms.

Some of the technologies used during the war were developed during the interwar years of the 1920s and 1930s; much was developed in response to needs and lessons learned during the war, while others were beginning to be developed as the war ended.
Many types of technology were customized for military use and major developments occurred across several fields including Weaponry, Logistical support Communications, and intelligence, Medicine Rocketry, and NDT were used to test all these parts or material or a system without impairing its future usefulness.

Visual Testing
The first and oldest nondestructive test method known today as visual testing (VT) used to determine the presence of visual surface imperfections. It is an important method in the broad field of nondestructive testing used to locate surface anomalies in most materials and subsurface discontinuities in translucent materials.

Radiography testing
Around 1895 Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen was a German mechanical engineer and physicist discovered X-Rays and was indented to be used in medical applications. Early technical X-ray applications in Germany were realized by Richard Seifert in around 1930. He improved X-Ray medical equipment with the cooperation of welding Institutes. After World War II Arturo Gilardoni in Italy, Drink, and Andreasen in Denmark developed X-ray-equipment, Kurt Sauerwein portable isotope-containers in Germany.
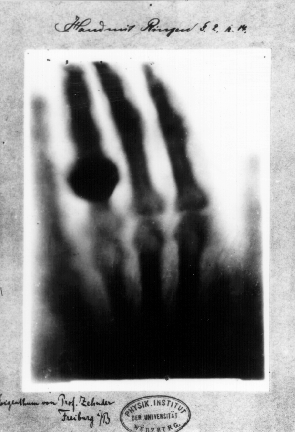
Radioisotopes were discovered by Madam Marie Curie, a Polish and naturalized-French physicist, and chemist received the Nobel-prize for physics in 1903 together with her husband Pierre Curie and Henri Becquerel. radioactive isotopes were initially used for medical applications. In Germany Rudolf Berthold and Otto Vaupel applied them after 1933 to welded joints.
Magnetic Particle Testing
Magnetism was first used as early as 1868 to check cannon barrel defects. Cannon barrels were first magnetized and then a magnetic compass was moved down the length of the barrel. If a discontinuity was present, the magnetic flux would leak out and cause the compass needle to move to indicate the location of defects.
In the early 1920s, William Hoke noticed metallic grindings from hard steel parts (held by a magnetic chuck while being ground) formed patterns that followed the cracks in the surface of parts he was machining on applying fine ferromagnetic powder to the parts, there was a build-up of powder at the discontinuities which formed a more visible indication.
The real industrial application was made by Victor de Forest and Foster Doane after 1929. They formed 1934 a company with the name Magnaflux in 1934, famous worldwide until today.
Penetrant Testing
In the early 1900s the oil and whiting method was used in the railroad industry, which included application of oil solvent for cleaning followed by chalk coating. The chalk coating absorbed oil from cracks making them easily visible. This became the principle for the method of crack detection using penetrants. During World War II the fast-growing aircraft-industry used more and more nonmagnetic light metals which could not be tested with Magnetic particle taking this into consideration, Magnaflux in Germany started production of fluorescent and dye penetrants.

Ultrasonic Testing
Around 1900, railroad workers tested objects by applying kerosene to the object and covering it with a coat o whiting. Then the object was struck with a mallet. In areas where the whiting looked wet, the object was assumed to be cracked. However, the methods of exciting ultrasound were discovered already in 1847 by James Precott Joule and in 1880 by Pierre Curie and his brother Paul Jacques.
Not earlier than 1912 a first the application was proposed after the “Titanic” had sunk. The Englishman Richardson claimed the identification of icebergs by ultrasound in his patent applications. In France, Chilowski and Langevin started their development to detect submarines by ultrasound during World War I. In 1929 the Russian Sokolov proposed to use ultrasound for testing castings
The detection of laminations in plates and fine non-metallic inclusions in hot-rolled profiles became necessary during World War II. The already existing NDT-methods – X-rays, MP, PT- were unable to solve these problems. In 1940s Floyd Firestone developed the first pulse-echo instrument for detecting deep-seated discontinuities.
There have been many developments in NDT methods in today’s industry and much more research is still going on.
Conclusion
SNT-TC-1A, the document for the qualification and certification of NDT personnel published by the American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT) is recommended practice for different levels of certification in different NDT methods about which we will learn in the coming days.

Non Destructive Testing FAQs:
What is NDT?
AS per ASME BPVC Article 1:
NON-DESTRUCTIVE EXAMINATION (NDE): THE DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION OF TECHNICAL METHODS TO EXAMINE MATERIALS AND/OR COMPONENTS IN WAYS THAT DO NOT IMPAIR FUTURE USEFULNESS AND SERVICEABILITY IN ORDER TO DETECT, LOCATE, MEASURE, INTERPRET AND EVALUATE FLAWS.
Who started NDT first in the world?
There are no precise dates recorded as to when NDT began as a recognized technology, human beings have performed nondestructive tests from their beginning. Centuries before the expression NDT was first used, people “looked” at objects to determine size, shape, and even the presence of visual surface imperfections and “listened” to the metal being shaped by a blacksmith or the tone of a bell after it was cast. World War II had the greatest effect on the technology and devices that are used today. World War II (often abbreviated to WWII or WW2), also known as the Second World War, was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. Technology also played a greater role in the conduct of World War II than in any other war in history and had a critical role in its final outcome. During this period different methods of NDT prominently came to use in the Mechanical world.
What is the meaning of NDT?
· NDT stands for Non Destructive Testing also addressed as nondestructive examination (NDE), nondestructive inspection (NDI), and nondestructive evaluation (NDE).
· It involves inspection of test object without cause any harm to the test object and without altering any properties of the test object.
· The test object under non destructive test does not undergo any change in its size., shape, physicals and chemical properties.
· It’s a wide group of analysis techniques used in different science and technology industries to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.
How many levels are there in NDT?
As per ASNT SNT-TC-1A, the document for the qualification and certification of NDT personnel. There are three different levels of certification which are
NDT Level I
NDT Level II
NDT Level III
What are the types of NDT methods?
There are six major NDT methods such as visual and optical aids , radiography, ultrasonic’s, eddy current , magnetic particle and dye penetrant , which are regularly used by industry in the various diagnostics application.
ASNT SNT-TC-1A, the document for the qualification and certification of NDT personnel carry out Certification of Personnel in following NDT methods:
· Acoustic Emission Testing
· Electromagnetic Testing
· Ground Penetrating Radar
· Guided Wave Testing
· Laser Testing Methods
· Leak Testing
· Liquid Penetrant Testing
· Magnetic Flux Leakage
· Magnetic Particle Testing
· Microwave Technology
· Neutron Radiography Testing
· Radiographic Testing
· Thermal/Infrared Testing
· Ultrasonic Testing
· Vibration Analysis
· Visual Testing
Why is NDT important?
· Because it allows one to inspect the quality of the material without impairing the aimed use or application of the test object.
· It is a fundamental and essential tool for control of quality of engineering materials, manufacturing processes, of reliability of products in services and maintenance of systems whose premature failure could be costly or disastrous.
· It has wide range of applications such as :
o Detection of flaws such as cracks , shrinkages, gas porosities, inclusions and other weld, forging and casting defects.
o Determining the material characteristics such as density, conductivity, hardness, grain structures etc. to provide data about the strength of materials,
o Dimensional measurements such as wall thickness , internal and outside dimensions , corrosion assessment coating/plating thickness etc.
Online monitoring of plants/industrial systems and in-service inspection of components.
To learn about Need of NDT in today’s world Read our blog:
NEED FOR NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING(NDT)
References :
https://www.nationalboard.org/Index.aspx?pageID=164&ID=377
https://app.aws.org/itrends/2005/07/021/
ASME NDT Handbooks



Pingback: Introduction to Eddy-current Testing(ECT) | World Of NDT
Thank you for your appreciation.
Hello, you used to write fantastic articles, but the last several posts have been kinda lackluster… I miss your super posts. Past few posts are just a little bit out of track!
Thank you for your feedback
We are trying to cover all the aspects of NDT. Still, we will work on your feedback.
Outstanding post, I think blog owners should larn a lot from this website its rattling user friendly .
Thank you for your feedback.
We will keep up the good work.
I have wanted to write about something like this on my webpage and you gave me an idea. Cheers.
Good to know that. Thank you for your feedback.
I discovered your blog site internet site on the search engines and check a few of your early posts. Always keep on the great operate. I simply additional encourage Feed to my MSN News Reader. Seeking forward to reading far more from you down the line!…
Thank you for your Feedback.
It’s difficult to get knowledgeable men and women with this topic, and you appear to be what happens you are dealing with! Thanks
Really appreciate your Feedback.
Thanks for your appreciation.
Saved as a favorite, I love your blog!
I loved your article.Much thanks again. Much obliged.
Really informative blog.Much thanks again. Great.
Pingback: Introduction to Acoustic emission testing | World Of NDT
Pingback: The Evolution of X-Ray Technology and Beginnings of NDT - ArticleCity.com