Introductio
n
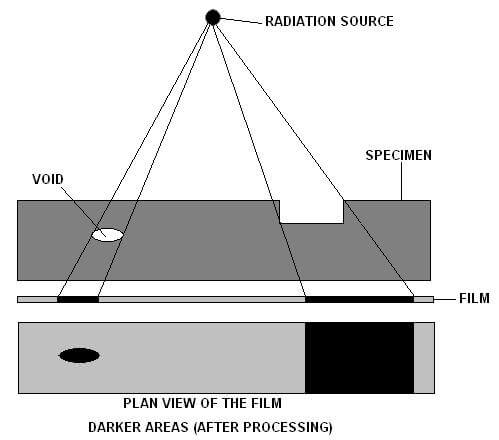
Radiography is a volumetric NDT test method used to determine internal flaws in castings and Welds. Radiographic testing includes passing of X-rays or Gamma Rays through the test item from one side and recording the rays on an imaging media on the other side giving a permanent visual record of the internal structure of the test items.
X-rays were initially developed for medical applications. To learn more about the history of radiography testing read our blog HISTORY OF NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING.
The Basic principle of Radiography Testing :
Radiography testing Uses the ability of x-rays and gamma rays to penetrate materials. X-rays and gamma rays can even penetrate materials that don’t transmit light. Penetration depends upon thickness, the density of material and size of source being used.
In passing through the material some of these rays get absorbed and transmitting the rest of the rays. These transmitted rays are recorded on an imaging media which on further processing gives a radiographic image of the test object.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
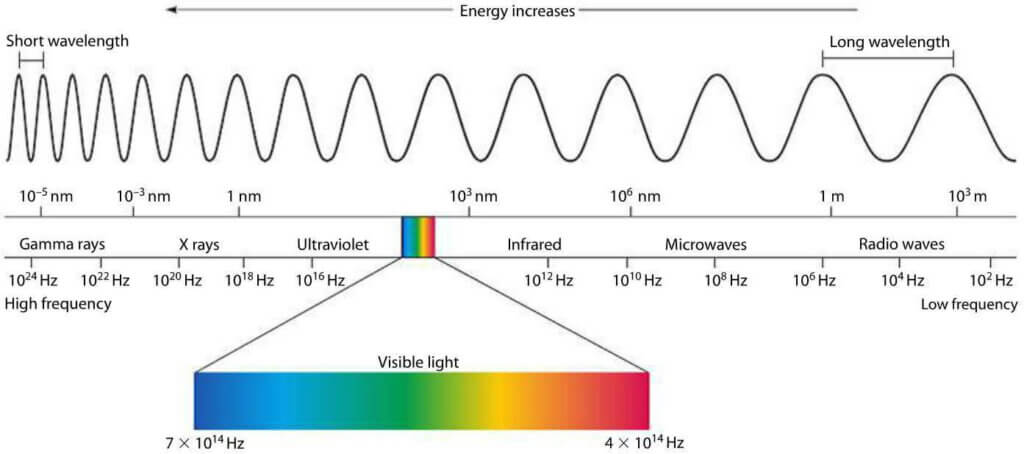
As you can see in the above chart X-rays and Gamma rays lie high energy, a short-wavelength portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Characteristics of X-ray and Gamma Rays
- have a wavelength inversely proportional to their energy.
- neither have electrical charges nor rest mass.
- travel at a velocity of light in the straight direction in free space.
- can penetrate matter where the depth of penetration depends upon the wavelength of radiation and the nature of the matter being penetrated.
- get absorbed as well as scattered by matter.
- They can ionize matter and can also expose the film/detector.
- They are not detectable by human senses.

Radiography test process
In order to carry out RT one need three things;
- Equipment that holds/generates X-rays or gamma rays.
- Test Object.
- Image recording media.
Equipment:
There are basically two types of radiography equipment:
- X-ray equipment
- Gamma Ray Equipment
X-ray Equipment
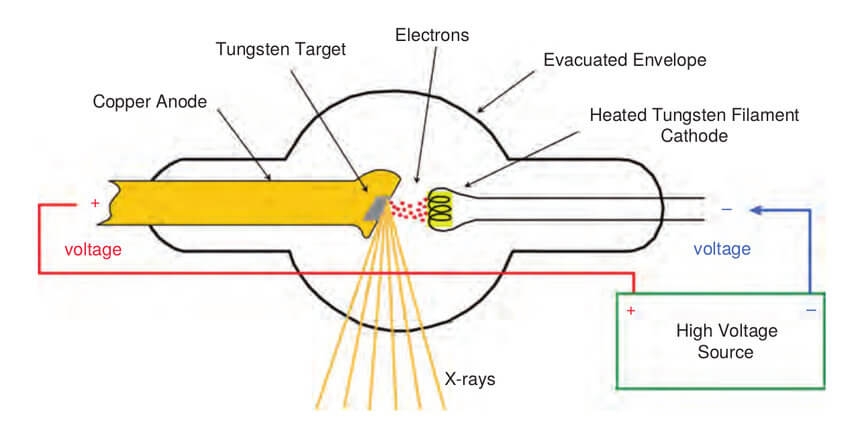
The Above figure shows an X-ray tube of X-ray equipment which consists of two electrodes (Cathode is the filament which functions as a source of free electrons and Anode houses the target which the electrons strike. ) enclosed in a heat resistant glass or ceramic vacuum envelope.
When current is passed through the cathode filament it starts getting hot. The heat emits electrons from the filament surface. The anode is positively charged hence it draws electrons emitted from the cathode. The potential difference between the cathode and anode is very high causing the electrons to flow from cathode to anode with very high energy.
When this high energy electron hits the tungsten atom of anode it removes an electron from lower orbitals of tungsten which is replaced by higher orbital electron simultaneously releasing its extra energy. This interaction of electrons between cathode and anode leads to generation X-rays.
Quick Fact: When the electrons collide with the target, about 1% of the resulting energy is emitted as X-rays, with the remaining 99% released as heat.
Gamma Ray Equipment :
It consists of a radioactive source that is placed in a shielded casing having an arrangement for in/out movement of the Radioactive source in a guide tube.
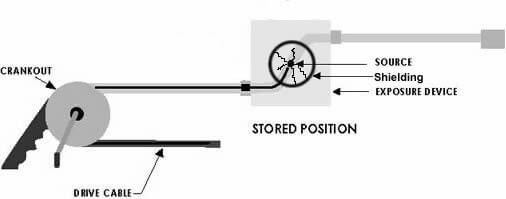
In the above figure, the rotation crank unit leads to forward and backward movement of the radioactive source in the tube coupled with the equipment called guide tube.
Cesium 137, Selenium 75 Iridium 192, Cobalt 60, Thulium 170 are commonly used artificially made radioactive materials in industrial radiography.
Quick Fact: all gamma-ray equipment used in industries are technically known as IGRED (industrial gamma-ray exposure device) and both X-ray and Gamma-ray equipment together are technically called IRED (Industrial radiation exposure device )
Image recording media :
It records the transmitted X-ray /Gamma Rays from the Test item and gives a radiographic image.
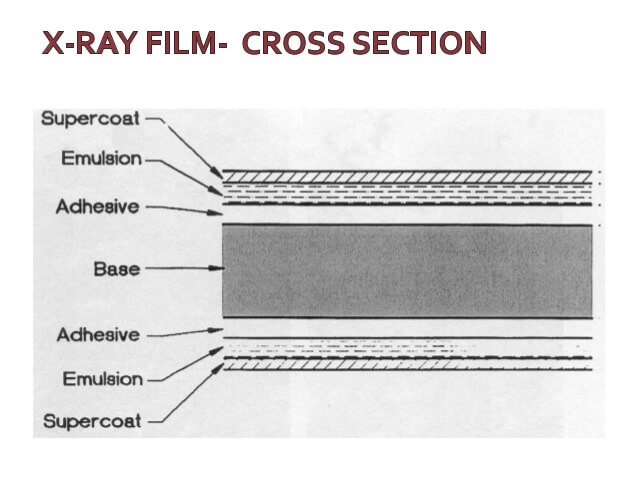
In film-based radiography, the films used to consist of a Polyester base with silver bromide and emulsion of gelatin coating bonded with the polyester base using an adhesive on both sides.
When transmitted Radiation hits this film. The film gets exposed making a latent image of the test item and further processing of this film gives the permanent radiographic image.
This processed film is called radiograph which is then interpreted and evaluated by certified professionals as per applicable code.
To know more about how to become a certified RT professional read our Blog: Beginners guide for becoming an NDT technician.
Conclusions
Applications of Radiography Testing:
- Testing and grading of welds on pressurized piping, pressure vessels, high-capacity storage containers, pipelines, and some structural welds.
- materials like concrete, welder’s test coupons, machined parts, plate metal, or pipe wall (locating anomalies due to corrosion or mechanical damage) can also be inspected using RT.
- can be used for the Testing of Non-metal components such as ceramics used in the aerospace industries is also regularly tested.
- Castings with a high service pressure


Advantages:
- Wide scope of application
- Provides permanent visual record.
- Volumetric inspection of materials
Limitations:
- Radiation safety procedures must always be followed.
- Both side accessibility of the test item is necessary
- Expensive
- Results are dependent on the orientation of discontinuity with respect to the radiation beam.
References:
https://www.miniphysics.com/electromagnetic-spectrum_25.html
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-general-concept-of-an-X-ray-tube-3_fig2_326106595/download
Wikipedia
ASNT RT classroom Training Book.

Pingback: Digital Radiography | World Of NDT
After checking out a handful of the articles on your website, I seriously like your technique of writing a blog. I bookmarked it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back soon. Take a look at my web site too and let me know what you think.
Appreciate you sharing, great blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
Thanks a lot for the blog article. Fantastic.
Major thanks for the article post.Really looking forward to read more. Much obliged.
A big thank you for your blog post.Really thank you! Much obliged.
Great article. Much obliged.
A big thank you for your blog article.Thanks Again. Really Cool.
Fantastic blog post. Much obliged.
Pingback: Radiographic Film Processing | World Of NDT
Are you looking for new radiography machines and c arm imaging equipment which give you a completely efficient workflow and also reduce the turn around time? Get one new imaging equipment for your facility with this link: https://www.uscultrasound.com/radiography/new-equipment/